2.3 STRATEGIC PRIORITY THREE: DELIVERING NEW STATISTICAL SOLUTIONS TO MAXIMISE THE VALUE OF PUBLIC DATA
2.3.1 Data integration and the Data Integration Partnership for Australia (DIPA) initiative
The ABS is a primary integrating authority for the Data Integration Partnership for Australia (DIPA). DIPA is a $130.8 million investment by the Government over three years to 2019–20 and is designed to maximise the use and value of the Government’s data assets. The ABS will receive $37.7 million over the three year period to identify and build the necessary data assets and supporting infrastructure required to support our partner agencies in their access to, and analysis of, integrated datasets.
Data integration and analysis creates new insights into complex policy questions, enabling effective evaluation of government policy and expenditure, and a richer picture of the dynamics of the economy.
Signature projects exemplifying the policy relevance of data integration include the following:
- informing the National School Resourcing Board review of existing school funding models to determine the efficient allocation of $145 billion of Commonwealth funds over the next 10 years (see Box 4);
- collaboration with the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare to develop an enduring, longitudinal linked justice dataset under the auspices of the Council of Australian Governments’ Prison to Work Report (2016);
- informing the Department of Industry, Innovation and Science’s investigation of the relationship between entrepreneurship and job creation in Australia;
- South Australian Employment Dynamics – using business datasets sourced from public administrative records to better understand aggregate employment and industry performance in South Australia;
- New South Wales Pathways – analysing how different pathways through upper secondary education, higher education and Vocational Education and Training compare in achieving educational attainment and engagement in work outcomes, considering factors such as socio-economic background and demographics, policy settings, regulatory frameworks and education and social policy programs;
- the Location Integration Capability, being developed by a partnership of Australian Government agencies, which will enable researchers to use data sets that are based on different measures of location to combine agricultural and other environmental data with social and economic information to inform policy.
BOX 4: INFORMING SCHOOL FUNDING MODELS
The Australian Government established the National School Resourcing Board (NSRB) to provide greater independent oversight over Commonwealth school funding. The NSRB asked the ABS to undertake a data linkage project to assist them to understand the socio-economic capacity of individual schools and, therefore, their capacity of the parent community to contribute financially to the running of their children’s school.
The Socio-economic characteristics of school catchments project examined the feasibility of integrating national datasets to investigate different models for estimating the socio-economic characteristics of non-government school catchment areas.
The Socio-economic characteristics of school catchments project comprised elements of the following datasets:
- Student Residential Addresses, 2012;
- Australian Census of Population and Housing, 2011; and
- Personal Income Tax (PIT), 2011–2012.The NSRB used the results of this work to make recommendations to Government.
The NSRB used the results of this work to make recommendations to Government. |
2.3.2 Environmental and satellite accounts
The ABS is supporting the Department of Energy and the Environment led National Approach to Environmental Accounting. The aim of the National Approach is to support complex decision making that involves environmental, economic and social dimensions. The strategy was endorsed by all Environment Ministers in early 2018. ABS will be delivering on priority accounting work around national land and waste accounts, as well as providing expertise on additional pilot projects.
The ABS is partnering with the Department of Infrastructure, Regional Development and Cities to produce an experimental Transport Satellite Account, due for release late in 2018. The experimental Transport Satellite Account will provide a comprehensive measure of transport services produced in the Australian economy. In addition to for-hire transport services, it will provide a measure of own-account or in-house transport services produced by businesses outside of the transport industry. The Transport Satellite Account will provide a measure of the economic contribution of transport services across the whole economy.
2.3.3 Alternate data sources
The ABS is exploring the potential usefulness of emerging big data sources for use in official statistics. Some current and evolving areas of work include:
- a partnership with Geoscience Australia to explore options for using satellite data to inform land accounts;
- along with our use of transactions data from retailers, extending web scraping for the compilation of the CPI (see section 2.1); and
- use of administrative and telematics data for insights in the use of vehicles and the road transport network (see section 2.5).
International experience suggests that administrative data has a lot to offer in how we can run a more efficient and potentially more valuable Census for the Australian community. Our research is investigating the potential of this data to:
- improve the quality of Census data;
- add new information to the Census;
- reduce the cost and burden of running the Census to taxpayers; and
- provide a contingency for areas affected by a natural disaster or other emergency event at Census time.
2.3.4 Communication, dissemination and microdata access
The ABS disseminates data publicly through a number of channels, but in particular through its website. The ABS has also made a concerted effort to increase awareness and informed use of our statistics through increased engagement with media and through our social media channels. As part of the SBTP, the ABS is designing a new website to make it easier to find, understand and use ABS information. In 2018–19 the ABS will launch a beta website designed to gather feedback from customers on our new website concepts as they evolve. Through the transformation investment the ABS is also developing Application Program Interface (API) services to enable systematic access to ABS data.
The challenge for the ABS is to enable access to more detailed and bespoke data sets that meet specific stakeholders’ needs which cannot be met through publicly releasing information. Safe and secure access to data is essential to maximise its public value, and the challenge for the ABS is to do so without risking confidentiality of the information. A balance is possible between the safe and effective use of microdata without compromising sensitive information.
Streamlining safe access for both government and academic researchers will continue to be a focus for the ABS in 2018–19.
While TableBuilder
1 will remain the primary means for accessing microdata (with over 1.2 million user sessions in 2017–18), the ABS is testing new innovative solutions.
The ABS DataLab, in particular, allows customers to access detailed confidentialised data directly in their own work environment. There are currently over 760 authorised users of the ABS DataLab, with around 70% of those users being from the government sector and the remainder a combination of education, private sector and community organisations.
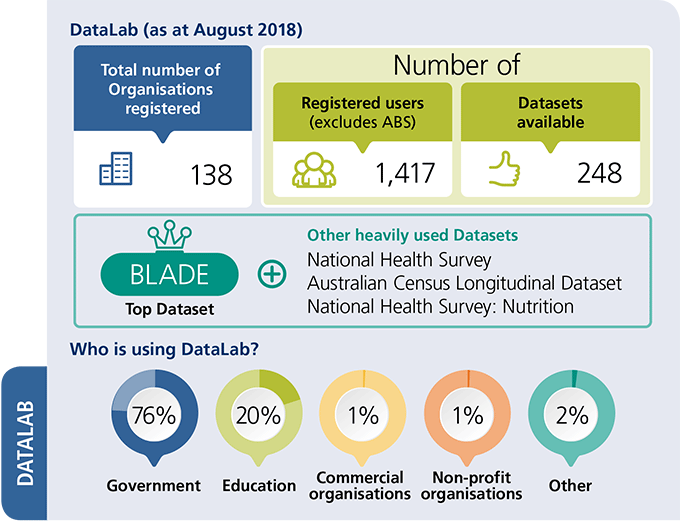
DataLab (as at August 2018):
- Total number of Organisations registered: 138
- Number of registered users (excludes ABS): 1,417
- Number of Datasets available: 248
- Top Dataset: Business Longitudinal Analysis Data Environment (BLADE)
- Other heavily used Datasets: National Health Survey, Australian Census Longitudinal Dataset, and National Health Survey: Nutrition
Who is using DataLab:
- Government: 76%
- Education: 20%
- Commercial organisations: 1%
- Non-profit organisations: 1%
- Other: 2%
 TableBuilder
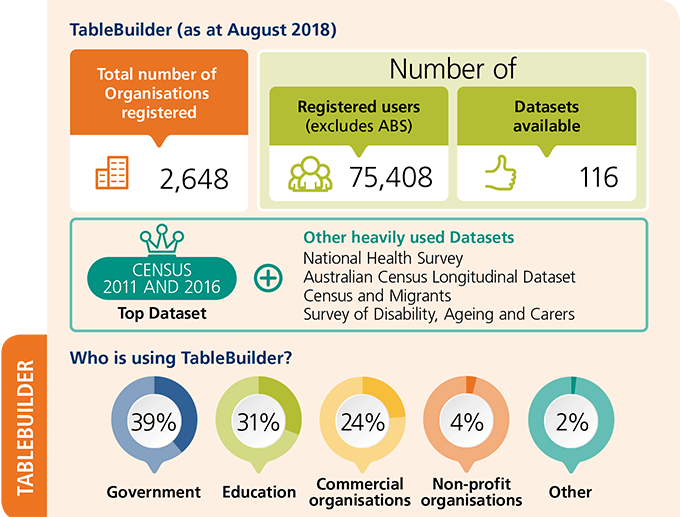
TableBuilder (as at August 2018):
- Total number of Organisations registered: 2,648
- Number of registered users (excludes ABS): 75,408
- Number of Datasets available: 116
- Top Dataset: Census 2011 and 2016
- Other heavily used Datasets: National Health Survey, Australian Census Longitudinal Dataset, Census and Migrants, and Survey of Disability, Ageing and Carers
Who is using TableBuilder:
- Government: 39%
- Education: 31%
- Commercial organisations: 24%
- Non-profit organisations: 4%
- Other: 2%
 1
1 TableBuilder is an online application that enables customers to interact and create customised tabular outputs from ABS data. TableBuilder features a unique confidentiality method that ensures all output data is confidentialised.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All